

In stem and leaf plots, tally marks are not required because the actual data are used. If the range of values is too great, the number 23.7 can be rounded up to 24 to limit the number of stems. Where observations are accurate to one or more decimal places, such as 23.7, the stem is 23 and the leaf is 7. If the observed value is 369, then the stem is 36 and the leaf is 9. These will be your leaves.įor example, if the observed value is 25, then the stem is 2 and the leaf is the 5.

On the other side of the line, write down the ones (the last digit of a number).Draw a line to the right of these stems.On the left hand side of the page, write down the thousands, hundreds or tens (all digits but the last one).Once you have decided that a stem and leaf plot is the best way to show your data, draw it as follows:
FIND OUTLIERS ON A STEM PLOT HOW TO
Top of Page Tips on how to draw a stem and leaf plot shows how the data are spread-that is, highest number, lowest number, most common number and outliers (a number that lies outside the main group of numbers).
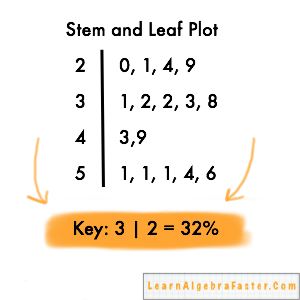 looks like a bar graph when it is turned on its side. For example, test results, speeds, heights, weights, etc. Anything that has a decimal point is rounded to the nearest whole number. shows the first digits of the number (thousands, hundreds or tens) as the stem and shows the last digit (ones) as the leaf. The leaf of the number will always be a single digit. The stem of the number includes all but the last digit. Each number in the data is broken down into a stem and a leaf, thus the name. A stem and leaf plot is used to organize data as they are collected.Ī stem and leaf plot looks something like a bar graph. Example 6 – Using stem and leaf plots as graphĪ stem and leaf plot, or stem plot, is a technique used to classify either discrete or continuous variables. Example 5 – Splitting stems using decimal values. Example 3 – Making an ordered stem and leaf plot. Example 2 – Making a stem and leaf plot. The main advantage of a stem and leaf plot. Example 1 – Making a stem and leaf plot.
looks like a bar graph when it is turned on its side. For example, test results, speeds, heights, weights, etc. Anything that has a decimal point is rounded to the nearest whole number. shows the first digits of the number (thousands, hundreds or tens) as the stem and shows the last digit (ones) as the leaf. The leaf of the number will always be a single digit. The stem of the number includes all but the last digit. Each number in the data is broken down into a stem and a leaf, thus the name. A stem and leaf plot is used to organize data as they are collected.Ī stem and leaf plot looks something like a bar graph. Example 6 – Using stem and leaf plots as graphĪ stem and leaf plot, or stem plot, is a technique used to classify either discrete or continuous variables. Example 5 – Splitting stems using decimal values. Example 3 – Making an ordered stem and leaf plot. Example 2 – Making a stem and leaf plot. The main advantage of a stem and leaf plot. Example 1 – Making a stem and leaf plot.  Tips on how to draw a stem and leaf plot. Please contact us to request a format other than those available. It is not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards and has not been altered or updated since it was archived. Bar graphs are especially useful when categorical data is being used.Information identified as archived is provided for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. Some bar graphs present bars clustered in groups of more than one (grouped bar graphs), and others show the bars divided into subparts to show cumulative effect (stacked bar graphs). One axis of the chart shows the specific categories being compared, and the other axis represents a discrete value. A bar graph is a chart that uses either horizontal or vertical bars to show comparisons among categories. That is, finding a general pattern in data sets including temperature, sales, employment, company profit or cost over a period of time. These graphs are useful for finding trends. A line graph is often used to represent a set of data values in which a quantity varies with time. The advantage in a stem-and-leaf plot is that all values are listed, unlike a histogram, which gives classes of data values. In a stem-and-leaf plot, all data values within a class are visible. The frequency points are connected using line segments.Ī stem-and-leaf plot is a way to plot data and look at the distribution. In the particular line graph shown in Example, the x-axis (horizontal axis) consists of data values and the y-axis (vertical axis) consists of frequency points. \): Atlanta Hawks Wins and Losses Number of WinsĪnother type of graph that is useful for specific data values is a line graph.
Tips on how to draw a stem and leaf plot. Please contact us to request a format other than those available. It is not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards and has not been altered or updated since it was archived. Bar graphs are especially useful when categorical data is being used.Information identified as archived is provided for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. Some bar graphs present bars clustered in groups of more than one (grouped bar graphs), and others show the bars divided into subparts to show cumulative effect (stacked bar graphs). One axis of the chart shows the specific categories being compared, and the other axis represents a discrete value. A bar graph is a chart that uses either horizontal or vertical bars to show comparisons among categories. That is, finding a general pattern in data sets including temperature, sales, employment, company profit or cost over a period of time. These graphs are useful for finding trends. A line graph is often used to represent a set of data values in which a quantity varies with time. The advantage in a stem-and-leaf plot is that all values are listed, unlike a histogram, which gives classes of data values. In a stem-and-leaf plot, all data values within a class are visible. The frequency points are connected using line segments.Ī stem-and-leaf plot is a way to plot data and look at the distribution. In the particular line graph shown in Example, the x-axis (horizontal axis) consists of data values and the y-axis (vertical axis) consists of frequency points. \): Atlanta Hawks Wins and Losses Number of WinsĪnother type of graph that is useful for specific data values is a line graph.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
